What Does Scabies Look Like On The Skin
Scabies
52298 34 Information forImages of Scabies



Overview
Scabies is an infestation of the skin acquired by a tiny mite called Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis. Scabies is very contagious and spreads rapidly in crowded areas such equally hospitals, nursing homes, child care facilities, prisons, and other locations where people spend extended periods of time in shut contact with one another.
The rash of scabies is extremely itchy and develops when a pregnant female mite burrows into the skin and lays her eggs. The human immune system is very sensitive to the presence of the mite and produces an allergic response that causes intense itching. Although a person who is infested with scabies ordinarily only has 10–xx mites on his or her entire trunk, there may be a large number of lesions because of this allergic response. Without treatment, the condition will non ordinarily improve.
Who'south at adventure?
Scabies is seen in people of all ethnicities, all ages, both sexes, and at all socioeconomic levels. The infestation is not caused by lack of personal hygiene but is more than often seen in people who live in crowded, urban conditions. People at particular risk are those who are in crowded living situations, such every bit hospitals, nursing homes, and prisons. Though scabies is extremely contagious, it usually requires prolonged skin-to-skin contact with a person who is already infested. Limited contact, such equally a hug or handshake, volition not normally spread the infection. However, scabies is easily spread to sexual partners and to other members of the household. Fifty-fifty if a person does not notwithstanding accept symptoms, he or she can pass the infestation on to other people. Less commonly, it may be spread past sharing towels, wear, or bedding.
Signs and Symptoms
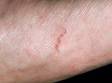
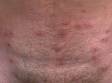
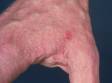
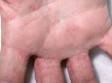
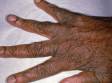
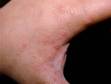
Although the entire body may itch, the most common locations for the lesions of scabies include:
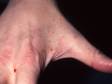
- The areas between the fingers (finger webs)
- Inner wrists, inner elbows, and armpits
- Breasts of females and ballocks of males
- Navel (umbilicus)
- Lower abdomen
- Buttocks
- Backs of knees
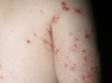
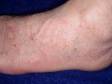
The most obvious signs of scabies are pink-to-scarlet bumps, which can await like pimples or bug bites, sometimes with scale or a scab on them. Even so, the tell-tale lesion of scabies is the burrow, which is small and often difficult to see. Typically, a burrow appears every bit a small, thread-like, scaly line (three–10 mm long), sometimes with a tiny black speck (the burrowing mite) at ane end. The adult mite is about 0.3 mm long and is very hard to see. Scabies mites clamber; they do not jump or fly.
People who are exposed to scabies may not develop itchy lesions for up to 6 weeks after becoming infested, as the immune organization takes some time to develop an allergic response to the mites. Yet, individuals who have had scabies before may develop the rash within several days of re-exposure.
Scabies is intensely itchy, especially at nighttime. Excessive scratching of the itchy lesions tin can create breaks in the pare, which may and so become infected with bacteria.
A astringent form of scabies, called Norwegian scabies or crusted scabies, is seen in:
- Elderly people
- Individuals with weakened allowed systems (such as organ transplant recipients or people with HIV/AIDS)
- Malnourished people
- People who are physically and/or mentally dumb or disabled
Self-Care Guidelines
Scabies requires prescription medication in order to stop the infestation. One time you lot are under a doctor's care, there are steps you can take to forestall scabies from coming back:
- Mites cannot survive off the human being trunk for more than 48–72 hours. Therefore, wash all clothing, bedding, and towels used by the infested person in the past 72 hours in hot h2o, and dry these items in a hot dryer.
- Vacuum all carpets, rugs, and furniture, and discard the vacuum bags.
- Put anything that cannot be laundered into plastic bags for at to the lowest degree 72 hours.
- Pets do not need to exist treated considering the mite simply lives on humans.
When to Seek Medical Care
See your medico if you develop an extremely itchy rash that does not go away. If other members of your household or people with whom you are in close contact accept like itchy rashes, they should also be evaluated by a medico.
Treatments Your Physician May Prescribe
Your medico may be able to diagnose scabies simply by examining your skin for typical lesions, such every bit burrows. Your doctor may too diagnose scabies past gently scraping some skin onto a slide and looking with a microscope for mites, eggs, or mite feces.
In almost cases of scabies, your doc volition prescribe a medicated cream or lotion to kill the infestation, such as:
- Permethrin 5% cream (Elimite®) – This is the first choice for treatment considering it is very constructive and condom. It is safe even for children and pregnant women. Rinse the foam off afterward 8–14 hours, and repeat in seven days to kill recently hatched larvae.
- Crotamiton 10% lotion or cream (Eurax®, Crotan®) – This is not as effective equally permethrin and can be irritating to the skin. Apply in one case daily for 5 sequent days.
- Precipitated sulfur (five% or 10%) – This is prepared with petroleum jelly and is practical nightly for 3 sequent nights. This is often the best choice for children aged younger than 2 years and for pregnant and lactating women considering it is very prophylactic to apply. Unfortunately, it is greasy, has an scent, and can stain clothing.
- Lindane 1% solution – Lindane can be toxic to the nervous arrangement. Therefore, avoid using information technology for young children and infants, significant or lactating women, and people with diseases affecting the fretfulness (neurological diseases). Apply to the body, rinse in eight hours, and echo in 7 days.
- For adults, apply to the entire body except for the confront and scalp.
- For children, employ to the entire body, including the face and scalp, equally these areas are ordinarily infested.
- Smear the production beneath the fingernails and toenails.
- Utilize to trunk folds, including within the navel, in the buttocks crease, and between the fingers and toes.
- Ivermectin (Stromectol®) pills – Have in one case and then repeat ane–2 weeks after. Practise non give to children aged younger than 5 years or who counterbalance less than fifteen kg (almost 35 lb), or pregnant or lactating women.
- Antibiotic, if whatsoever scratched areas appear to be infected with leaner.
Your doctor may besides recommend steroid creams or antihistamine pills to relieve the itching. In severe cases, oral steroids may exist required to decrease symptoms.
Because it may take up to half dozen weeks after exposure to develop symptoms, people may be unaware that they are infested. Therefore, household members, sexual partners, and anyone else with prolonged skin-to-skin contact with an infested person should besides exist treated. Ideally, everyone should be treated at the aforementioned time in society to prevent reinfestation.
Trusted Links
MedlinePlus: ScabiesClinical Data and Differential Diagnosis of ScabiesReferences
e Control and Prevention. Scabies. http://world wide web.cdc.gov/scabies/index.html. Modified November 10, 2008. Accessed March eleven, 2009.
Bolognia, Jean L., ed. Dermatology, pp.1321-1324. New York: Mosby, 2003.
Freedberg, Irwin M., ed. Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine. vith ed. pp.1374, 1394, 2283-2284. New York: McGraw-Loma, 2003.
Source: https://www.skinsight.com/skin-conditions/adult/scabies
Posted by: tuttlespeliveral.blogspot.com



0 Response to "What Does Scabies Look Like On The Skin"
Post a Comment